Candida Albicans is a type of yeast, well documented to be found in healthy mouths and as part of the normal mucosal flora. This yeast is normally found in small amounts within the mouth and digestive tract, but it can become a problem if allowed to overgrow. Candida can easily grow and create a white coating on your tongue, or even worse when the immune system is weakened. Yeast infection can also target other parts of your mouth. Although oral thrush can be painful, it is usually not life-threatening and will normally resolve with treatment.
Oral candidiasis have a wide range of symptoms. Meningitis is an extremely rare complication of thrush, but most often people develop white or cream colored patches inside their mouth which wipe away to reveal a red and inflamed tissue. They may also be painful, cause a cottony feeling in the mouth, and lead to difficulty in swallowing. In more extreme instances, there may be cracks at the mouth corners and a burning feeling. Oral thrush can have similar symptoms to other conditions which could impact the mouth, so it is essential that someone visit a health care professional for accurate diagnosis.
Oral candidiasis results from a number of factors. Individuals with immune – compromised systems are more likely to develop the condition, as their bodies have less capacity for controlling Candida growth. That means people who are getting chemotherapy for cancer, AIDS (HIV) patients, and others whose normal ability to fight germs is lower. Poor oral hygiene, use of dentures (which occur to 44-86% thrush) smoking-INHALED CORTICOSTEROIDS for asthma are other risk-factors. Antibiotic use can also predispose to the development by altering that all-important balance of beneficial bacteria. Infants, diabetics and the elderly are particularly exposed to risk since they have immune systems are more susceptible.
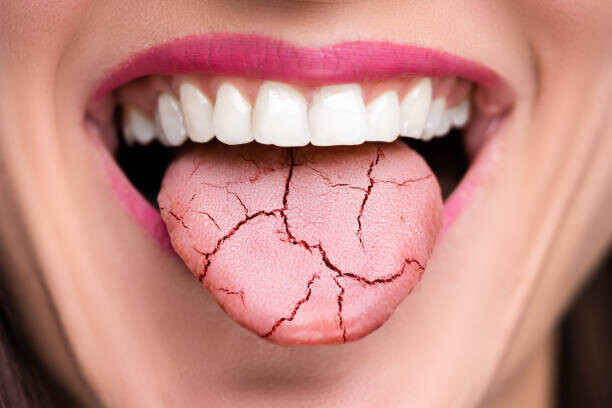

Treatments for oral candidiasis, which is a fungal infection of the mouth, often involve antifungals prescription, which can be in the form of an oral tablet, lozenge or mouth rinse. The function of these drugs is to lower Candida overgrowth and eliminate signs. In mild cases, home remedies could also aid. Practicing good dental hygiene (brushing teeth, tongue and antiseptic mouthwash) can help control the infection. When it hurts and white patches have formed, rinse your mouth with a solution of lukewarm water and salt; this can also help reduce fungal growth. Also, cut back on sugar and avoid alcohol or tobacco as this will prevent more irritation. In most cases, Candida can be treated effectively with a short course of medication or temporary changes in diet.
Genital Candidiasis: Prevention and Care

What Is Genital Candidiasis or Yeast Infection? This overgrowth usually happens when the natural balance of bacteria and fungi leads to all sorts of troubles in a woman’s nether regions. Although it is a benign condition and not serious in nature, men as well as women are affected leaving very uncomfortable symptoms that can be tough to deal with. We need to correctly asses the root causes and conditions that give rise of genital candidiasis in order to provide an effective and preventive care management.
Genital candidiasis symptoms: Someone with genital candidiasis may experience redness, burning and itching, in the vaginal or penile area with thick white discharge. Irritation and redness near the tip of penis (in men) When these symptoms start to show, it is important that you consult a doctor to diagnose this serious condition accurately. Usually diagnosis is achieved based on a physical examination and laboratory tests showing that the levels of Candida fungi (yeast) are higher than normal.
Genital yeast infection is not just a genital skin problem; there are many factors that trigger this recurrent candidiasis, which goes beyond simple lifestyle to underlying systemic causes. Wearing tight-fitting, non-breathable clothing or synthetic underwear may encourage the growth of Candida in your genital area. You can get a yeast infection if you are taking antibiotics because the meds kill not just bad bacteria, but good ones that keep other bugs in check and make sure your vagina is healthy. Individuals with hormonal changes (like during pregnancy or an IVF cycle), high blood sugar & type 2 diabetes keep getting themselves infected again. If you have diabetes or a weakened immune system, it is important to be extra wary of Candida overgrowth since your blood sugar levels might help Candida to strive. Even more so, antibiotics will kill the good bacteria in our body that keeps us free from harmful bacteria which allows Candida to grow.
Genital candidiasis prevention: Lots of changes in the lifestyle should be applied to help you keep a balance of microorganisms within genital region thereby prevent occurrence. If you suffer a recurrent irritation then wear loose cotton underwear, avoid douching or scented hygiene products. It is also important to keep the area clean and dry. Those who have had recurring yeast infections, however, may find it wise to be proactive and add probiotics to your diet as these good bacteria can keep a body in balance. When an infection does happen, antifungal creams or oral medications can be used to treat it as well as home remedies like yogurt (probably the best way) or tea tree oil.
Prevent and care for genital candidiasis in our day to day requires that we be proactive, adopting small changes of habit gives more balance and health obtaining improvements in quality of life by avoiding recurrences.
Skin Candidiasis: Managing Infections on the Skin
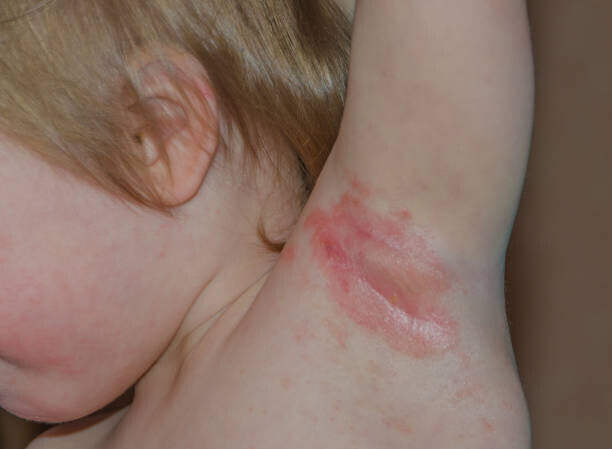
Skin Candidiasis is a common fungal infection that occurs when there are abnormal overgrowth of the yeast called candida on the skin. This can crop up anywhere (in a warm, moist environment where the fungus is) around your body. Although it may not sound like a big deal, skin candidiasis can be very irritating and if allowed to progress untreated then more serious issues can occur. Knowing how to deal with and prevent skin candidiasis is very important in keeping your skin healthy.
Skin candidiasis can appear in different forms and plague adults or children. One of the most common types is that which affects babies, diaper rash associated with extended sitting inside a warm and moist environment (diaper area). A type that is usually found here; i.e. Intertrigo, which affects skin folds (groin, under breasts) where friction and trapped moisture provide perfect conditions for yeast proliferation. Intertrigo develops in people who are overweight or have diabetes and who are exposed to excessive amounts of sweat.
The symptoms of skin candidiasis can change depending on the area that is infected and how severe the infection has become. Some individuals experience redness, itchiness or burning in the infected area. There may be swelling and little red bumps, or sores formed on the skin as well. In some cases, skin may even crack and ooze or scale up. Areas where skin folds (e.g., the groin, armpit or under targeting toes) are most affected as these areas tend to be warmer and provided with more moisture.
Skin candidiasis treatment includes antifungal medications to use on the skin, and lifestyle changes that can help reduce yeast growth. Topical antifungal creams may be recommended for benign infections, however a doctor will likely prescribe systemic drugs (either topical or oral) in more chronic cases to provide relief. Maintain excellent hygiene to keep the impacted location dry. Wearing loose fitting clothes, changes in dry garments and using powders or antiperspirant can help reduce moisture.
Proper hygiene and skin moisture control are the two most important aspects that contribute to preventing this type of candidiasis. Using breathable clothes like cotton also helps to keep the skin dry. Eating right and incorporating probiotics into your diet may help keep the overall numbers of unhealthy bacteria in balance if they are out of alignment, although you cannot use them as a stand-alone solution. By identifying the causes and knowing your treatment options, you can take steps to avoid future episodes of infection and keep skin in good condition.
Invasive Candidiasis: Understanding Severe Infections

Invasive Candidiasis is a severe and sometimes life-threatening condition that occurs when the Candida fungus, part of the human microbiome present in small quantities, escapes into the bloodstream or deeper tissues. It differs from common yeast infections in the skin or mucous and can affect internal organs such as the heart, kidneys, or liver. For this reason, it is a serious condition that requires rapid medical intervention as it can be accompanied by serious complications when left untreated. We should understand the nature of invasive candidiasis to recognize its symptoms and to take timely actions. Seek medical attention urgently if any symptoms suggest infection. Symptoms range from organ symptoms and general appearance to such infections as fungal infections of vital organs. Again, it should be noted that many of the first symptoms are not signs of a disease .
At the beginning of the infection, which affects the whole organism, general illness, and fever can often be observed, and other symptoms appear much later. A wide range of symptoms is also related to specific signs of organ involvement in the disease. There are several key signs of invasive candidiasis. Fever and chills that are sustained in response to antibiotics are the ones. They are accompanied by a state of general illness. They can be complementary to localized manifestations in which the infected area hurts. Symptoms may be milder at the beginning of the infection; other symptoms may occur later with more pathological center manifestations; these symptoms may be complications of organ dysfunction. There are many conditions that predispose a person to this infection. Worsening immune function, critical illness such as chemotherapy, HIV/AIDS; there is a severe infection after major surgery, protracted hospital stay with frequent stays in the intensive care unit.
C. Albicans disrupts the body’s defense mechanisms over normal “good” bacteria and can cause infection when using central IV indwelling catheters or using a large amount of antibiotic; a, malnutrition, parenteral nutrition in premature infants and fatalities. Fast treatment of ICI (Invasive Candidiasis) with antifungal drugs taken from a venous catheter in the hospital, such treatment can be critical; antibiotics can be removed; treatment should start with antibiotics.
Summary Statement signs and clear understanding of risk factors for invasive candidiasis is key contribution factor; this leads to the need for timely diagnosis and intervention. Exposure to care cannot be overlooked for invasive candidiasis; serious steps to treat this disease should be taken on spot as it might lead to severe health problems.
Thank you for reading my article about “Types of Candidiasis” and I would love to receive your comments down below, in case of any.